在本系列的早期,我们了解了如何设置 Truffle 并用它来编译,部署Bounties.sol 合约并与其进行交互。
本文将介绍在 Truffle 框架内为智能合约编写测试所需的操作。Truffle 项目中的测试可以用 Javascript 或 Solidity 编写,本文将重点介绍 Javascript 测试。
Truffle 使用 Mocha 测试框架提供了一种用Javascript 编写测试的简单方法,并使用Chai 进行断言( assertions)。您可以在此处阅读有关Truffle测试 的更多信息。
本教程的源代码在此处 可以找到。
先决条件Prerequisites
NODEJS 7.6+
由于 web3.js 和 truffle executios 是异步的,我们会使用async /await 来简化测试代码。你必须升级到Node 7.6或更高版本。
TRUFFLE
$ npm install -g truffle
更多详情可参考安装truffle。
Truffle 工程
为了测试 Bounties.sol 智能合约,我们需要设置一个truffle 工程来编译和部署。让我们从该系列之前创建的 truffle 工程开始:
$ git clone https://github.com/kauri-io/kauri-fullstack-dapp-tutorial-series.git $ cd kauri-fullstack-dapp-tutorial-series $ cp -R truffle-compilation-and-deploy dapp-series-bounties $ cd dapp-series-bounties
我们还需要安装 truffle-hdwallet-provider 依赖项,以确保项目编译:
$ npm install truffle-hdwallet-provider@web3-one --save
开发区块链: Ganache-CLI
为了部署智能合约,我们需要一个以太坊环境。为此,我们将使用 Ganache-CLI 运行本地开发环境。
注意:如果您用的是Windows,需要先安装Windows开发人员工具
npm install -g windows-build-tools
$ npm install -g ganache-cli
针对windows用户的提醒:
你还需要安装 promise 和 bindings 以避免出错。
npm install mz
npm install bindings
建立测试文件
现在工程设置已经完成了,下面将创建第一个测试:
- 首先,我们需要在/test 文件夹中创建一个名为 bounties.js 的文件
- 在 bounties.js 文件中,我们需要导入Bounties.sol,以便在测试中用到它
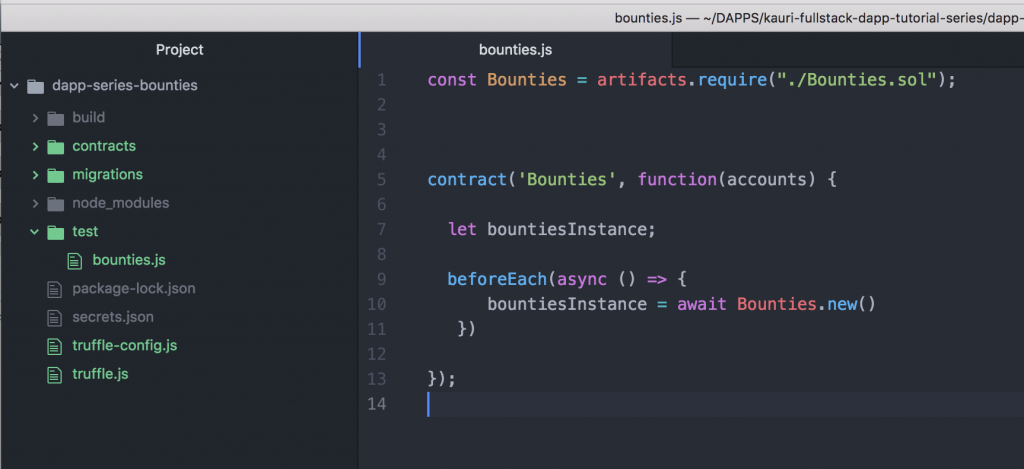
const Bounties = artifacts.require("./Bounties.sol");
- 我们现在将定义一个合约容器,对合约的测试会在容器中运行。通常将其设置为合约的名称,不过这不是必需的,你也可以随你心情起名。
contract('Bounties', function(accounts) {
let bountiesInstance;
beforeEach(async () => {
bountiesInstance = await Bounties.new()
})
})
- 在合约容器中,我们还定义了一个变量,以此保存被测试的合约实例 bountiesInstance 和一个 beforeEach 区块
- beforeEach 区块将在每次测试之前执行,并将部署 Bounties.sol 智能合约的新实例。这可确保每个测试都是在干净的合约状态(a clean contract state)下执行
您的 bounties.js 文件应如下所示:
现在我们有了测试文件的基本框架,可以通过执行以下操作来测试所有设置是否正确:
首先在一个单独的窗口中启动 ganache-cli :
$ ganache-cli
接下来,运行 truffle test 命令:
$ truffle test
运行truffle test 会执行truffle项目 /test 文件夹中的所有测试。具体如下:
- 编译你的合约
- 运行部署合约(migrations )以将合约部署到网络
- 针对网络上部署的合约运行测试
编写测试
先看下 issueBounty 函数:
function issueBounty(
string _data,
uint64 _deadline
)
external
payable
hasValue()
validateDeadline(_deadline)
returns (uint)
{
bounties.push(Bounty(msg.sender, _deadline, _data, BountyStatus.CREATED, msg.value));
emit BountyIssued(bounties.length - 1,msg.sender, msg.value, _data);
return (bounties.length - 1);
}
我们想在这个函数中测试一些东西:
- happy path:发放奖励(bounty)时应发出 BountyIssued 事件
- happy path:调用 issueBounty 应该返回一个整数
- payable 关键字:在不发送值的情况下发放奖励会失败
- hasValue 修饰符:发出奖励值为0的话会失败
- validateDeadline 修饰符:发布截止日期不大于现在会失败
辅助函数
我们期望如果输入验证失败,EVM能返回错误。您可以在此处阅读有关Solidity中错误处理的更多信息。
另外,要创建奖励,我们需要传递一个大于EVM当前时间戳的截止日期。
为此,我们需要编写一些辅助函数来帮助我们编写测试:
- 首先,在 /test 目录下创建一个 utils 文件夹,并创建一个文件 time.js
- 将以下内容复制到 time.js 中
function getCurrentTime() {
return new Promise(function(resolve) {
web3.eth.getBlock("latest").then(function(block) {
resolve(block.timestamp)
});
})
}
Object.assign(exports, {
getCurrentTime
});
上面的内容使用 web3 库从EVM中获取最新的区块,并返回其时间戳。
- 在/test/utils 目录中创建一个名为 assertRevert.js 的文件
- 将以下内容复制到 assertRevert.js 中
var assertRevert = async (promise, message) => {
let noFailureMessage;
try {
await promise;
if (!message) {
noFailureMessage = 'Expected revert not received'
} else {
noFailureMessage = message;
}
assert.fail();
} catch (error) {
if (noFailureMessage) {
assert.fail(0, 1, message);
}
const revertFound = error.message.search('revert') >= 0;
assert(revertFound, `Expected "revert", got ${error} instead`);
}
};
Object.assign(exports, {
assertRevert
}
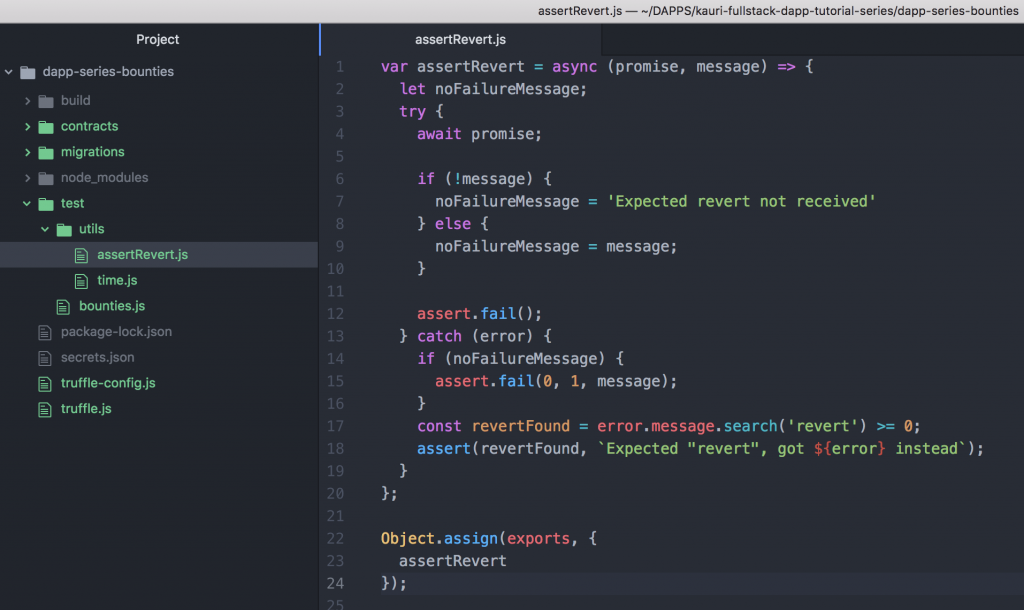
上面的内容将promise 作为第一个参数,它将是一个web3事务,而断言失败消息( assertion fail message )作为下一个。 try语句处理promise,并捕捉错误。如果promise 失败,它会检查错误消息是否包含字符串“revert”。
我们通过将下面几行添加到 bounties.js 测试文件,这样就能导入辅助函数了:
const getCurrentTime = require('./utils/time').getCurrentTime;
const assertRevert = require('./utils/assertRevert').assertRevert;
const dayInSeconds = 86400;
我们还添加了 dayInSeconds 常量,以帮助我们添加天数。
Happy Path
注意:以下所有测试都应放在 bounties.js 文件中
我们的第一个 happy path 的测试看起来像这样:
it("Should allow a user to issue a new bounty", async () => {
let time = await getCurrentTime()
let tx = await bountiesInstance.issueBounty("data",
time + (dayInSeconds * 2),
{from: accounts[0], value: 500000000000});
assert.strictEqual(tx.receipt.logs.length, 1, "issueBounty() call did not log 1 event");
assert.strictEqual(tx.logs.length, 1, "issueBounty() call did not log 1 event");
const logBountyIssued = tx.logs[0];
assert.strictEqual(logBountyIssued.event, "BountyIssued", "issueBounty() call did not log event BountyIssued");
assert.strictEqual(logBountyIssued.args.bounty_id.toNumber(),0, "BountyIssued event logged did not have expected bounty_Id");
assert.strictEqual(logBountyIssued.args.issuer, accounts[0], "BountyIssued event logged did not have expected issuer");
assert.strictEqual(logBountyIssued.args.amount.toNumber(),500000000000, "BountyIssued event logged did not have expected amount");
})
显示内容很多,但很简单:
- 每个测试都以函数 it() 开始,它将测试的描述作为其第一个参数,并将回调函数作为下一个参数。我们使用 async() 作为回调,因此我们可以使用await
- 然后使用getCurrentTIme() 作为帮助器(helper),针对bountiesInstance 对象调用issueBounty交易,以确保我们的截止日期有效
- 该交易从帐户[0]发送,值为500000000000000000
- 然后我们断言我们的交易收据包含一个记录了1个事件的日志
- 然后我们断言事件的细节与预期相符
我们测试调用issueBounty (而不是发送交易)的第二个 happy path 如下所示:
it("Should return an integer when calling issueBounty", async () => {
let time = await getCurrentTime()
let result = await bountiesInstance.issueBounty.call("data",
time + (dayInSeconds * 2),
{from: accounts[0], value: 500000000000});
assert.strictEqual(result.toNumber(), 0, "issueBounty() call did not return correct id");
});
在上面我们将.call 添加到issueBounty来调用函数(而不是发出交易)。这将返回函数的返回值,而不是交易接收。
注意:因为结果是 BigNumber 类型,我们还需要在断言函数中调用.toNumber()。
Error Path
错误路径(error path)测试是将一个带有无效输入的交易作为断言函数的参数。
为了测试我们的可支付(payable)关键字,我们调用一个没有设置值的交易:
it("Should not allow a user to issue a bounty without sending ETH", async () => {
let time = await getCurrentTime()
assertRevert(bountiesInstance.issueBounty("data",
time + (dayInSeconds * 2),
{from: accounts[0]}), "Bounty issued without sending ETH");
});
要测试 hasValue() 修饰符,我们使用值0调用我们的交易:
it("Should not allow a user to issue a bounty when sending value of 0", async () => {
let time = await getCurrentTime()
assertRevert(bountiesInstance.issueBounty("data",
time + (dayInSeconds * 2),
{from: accounts[0], value: 0}), "Bounty issued when sending value of 0");
});
要测试我们的 validateDeadline 修饰符,我们需要发送两个交易,一个截止日期设置为过去,另一个截止日期设置为现在:
it("Should not allow a user to issue a bounty with a deadline in the past", async () => {
let time = await getCurrentTime()
assertRevert(bountiesInstance.issueBounty("data",
time - 1,
{from: accounts[0], value: 0}), "Bounty issued with deadline in the past");
});
it("Should not allow a user to issue a bounty with a deadline of now", async () => {
let time = await getCurrentTime()
assertRevert(bountiesInstance.issueBounty("data",
time,
{from: accounts[0], value: 0}), "Bounty issued with deadline of now");
});
现在如果运行truffle test 命令,我们应该看到以下内容:
$ truffle test
Compiling ./contracts/Bounties.sol...
Compiling ./contracts/Migrations.sol...
Contract: Bounties
✓ Should allow a user to issue a new bounty (207ms)
✓ Should return an integer when calling issueBounty (142ms)
✓ Should not allow a user to issue a bounty without sending ETH (116ms)
✓ Should not allow a user to issue a bounty when sending value of 0 (100ms)
✓ Should not allow a user to issue a bounty with a deadline in the past (109ms)
✓ Should not allow a user to issue a bounty with a deadline of now (110ms)
6 passing
Time travel
主要测试中,还有一项是检查截止日期,如果日期已过,则合约不接受履行。为了测试这个,我们需要添加一个辅助函数来提前EVM的时间戳:
在 /test/utils/time.js 文件中添加以下内容:
function increaseTimeInSeconds(increaseInSeconds) {
return new Promise(function(resolve) {
web3.currentProvider.send({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
method: "evm_increaseTime",
params: [increaseInSeconds],
id: new Date().getTime()
}, resolve);
});
};
此函数调用ganache EVM 的evm_increaseTime RPC 函数,以提前EVM 的区块时间戳。
将新的 increaseTimeInSeconds 函数添加到文件的exports 部分:
Object.assign(exports, {
increaseTimeInSeconds,
getCurrentTime
});
在bounties.js 测试文件中,添加以下内容来导入新辅助函数:
const increaseTimeInSeconds = require('./utils/time').increaseTimeInSeconds;
现在可以在测试中使用它了,如下所示:
it("Should not allow a user to fulfil an existing bounty where the deadline has passed", async () => {
let time = await getCurrentTime()
await bountiesInstance.issueBounty("data",
time+ (dayInSeconds * 2),
{from: accounts[0], value: 500000000000});
await increaseTimeInSeconds((dayInSeconds * 2)+1)
assertRevert(bountiesInstance.fulfillBounty(0,"data",{from: accounts[1]}), "Fulfillment accepted when deadline has passed");
}
自己试一下
既然您已经了解了如何测试 issueBounty 函数,请尝试为以下函数添加测试:
- fulfilBounty
- acceptFulfilment
- cancelBounty
可阅读源代码以了解更多信息。

